Introduction to Python
Python is a widely used programming language that is intuitive and easy to learn. From researchers to independent developers to large companies such as Facebook and DropBox: they all rely on Python. And for good reasons!
In this course, which consists of eight chapters, you will learn how to program in Python! You will start with the syntax, which are the rules of grammar for a programming language, and from there work your way towards more advanced features of the language. At the end of this course, you will have a solid understanding of Python, and you will be ready to apply that understanding to specific topics, such as software development and data science!
In this course, you will learn
- The rules (syntax) of the Python language
- How to structure your code with loops and functions
- How to import modules
- How to handle errors in your code
- How to work with files and folders

Figure 1. Your friendly Python teacher
Installing and using Python
Let's start by getting you set up, That is, let's see how you can install and use Python, and which version of Python you should use.
Python 2 or 3?
There are two main versions of Python: 2 and 3. The recommended version is Python 3, which is newer and actively maintained. Python 3 has many secondary versions, such as Python 3.10. For the purpose of this course, any recent version of Python 3 will do.
Python 2 is still used occasionally, but only because certain Python libraries have not yet been updated to be compatible with Python 3. We will not use Python 2 in this course.
Interactive mini exercises in the browser
Most chapters in this course contain interactive mini exercises. These consist of a problem to solve, and a small editor in which you can enter your solution in the form of Python code. You can click the Run button to execute your code, and the output appears in a box below. In most cases, your solution will be checked automatically.
Try it!
Mini exercise
Click on the Run button to execute the code and solve this mini exercise!
Code editors for Python
The mini exercises on this website are a convenient way to practice your Python skills. However, they are not suitable for real-life programming. Therefore, if you want to use Python for real-life programming, you will need a code editor with a Python environment, such as Rapunzel or Spyder.
Rapunzel
Rapunzel is a free code editor focused on numerical computing with Python. You can also download it as a standalone application from here (it is also included with OpenSesame):
In Rapunzel, create an empty document (Ctrl+N) and enter the code print('Hello world!') in the editor window. Next, press F9 to execute (Figure 2). This will execute this line of code in the so-called IPython Console, which by default is on the bottom of the window. You can also type directly into this console.
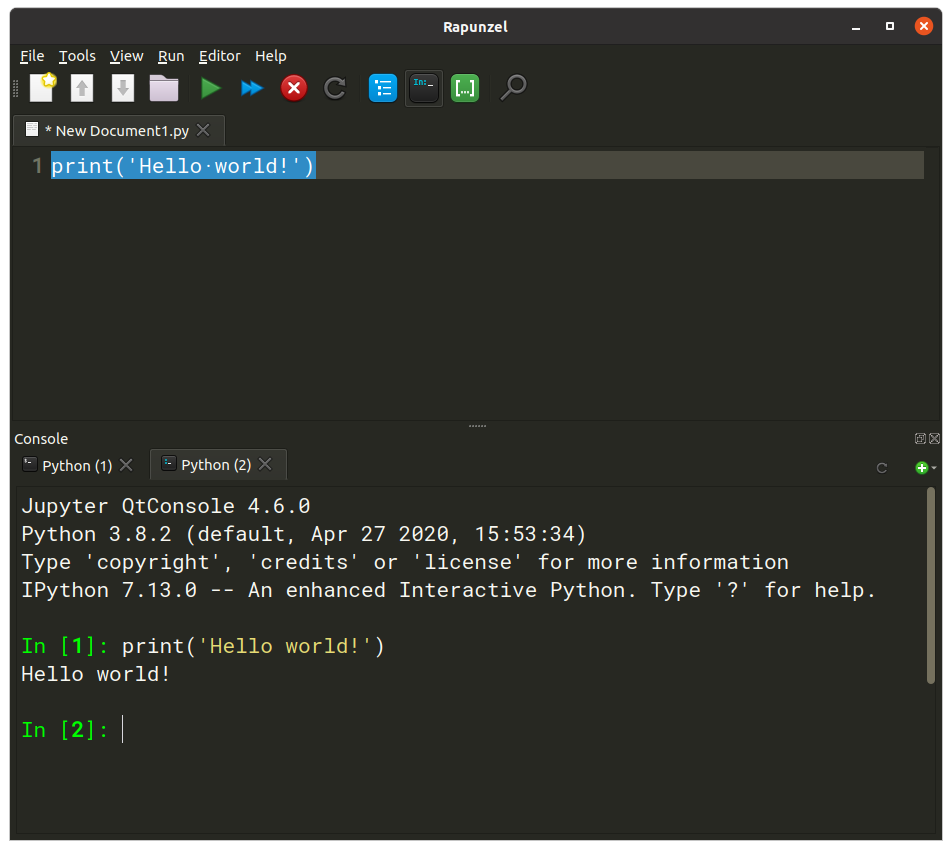
Figure 2. Printing 'Hello world' to the IPython console in Rapunzel.
Spyder / Anaconda
Anaconda is a Python distribution that comes with many useful packages pre-installed. Notably, it comes with Spyder pre-installed, which is another popular code editor for Python.
- Visit http://anaconda.org/, click on Download Anaconda, and download the 64 bit version for Python 3.
- Once the
.exeinstaller has been downloaded, launch it and follow the steps to install Anaconda on your system. The default installation settings are generally fine. - Now launch Spyder, which has been installed as part of Anaconda.
In Spyder, enter the code print('Hello world!') in the editor window, select it and press F9 to execute (Figure 3). This will execute this line of code in the so-called IPython Console, which by default is on the bottom-right of the window. You can also type directly into this console.
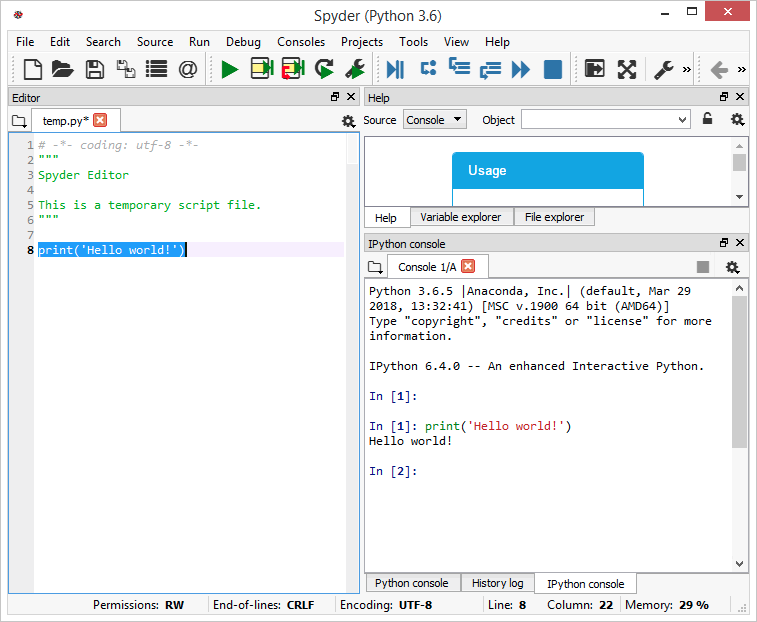
Figure 3. Printing 'Hello world' to the IPython console in Spyder.
Course overview
All set up? Then let's get started! This course consists of eight chapters. Each chapter builds on the previous chapters, so it is recommended to follow the chapters in order.
- Introduction to Python (this chapter)
- Syntax
- Iterables: list, dict, and tuple
- Loops: for and while
- Functions
- Modules
- Exceptions: error handling
- Files and folders
You're done with this section!
Continue with Syntax >>
